For many years my setup was pretty simple: A FreeBSD home server running on my old laptop. It runs everything I need to be present on the internet, an email server, a web server (like the one you’ve accessed right now to see this blog post) and a public chat server (XMPP/Jabber) so I can be in touch with friends.
For my home network, I had a basic Access Point and a basic Router.
Lately, my setup has become more… intense. I have IPv6 thanks to Hurricane Electric, the network is passed to my home network (which we’ll talk about in a bit), a home network with multiple VLANs, since friends who come home also need WiFi.
I decided to blog about the details, hoping it would help someone in the future.
I’ll start with the simplest one.
The Home Server
I’ve been running home servers for a long time. I believe that every person/family needs a home server. Forget about buying your kids iPads and Smartphones. Their first devices should be a real computer (sorry Apple, iOS devices are still just a toy) like a desktop/laptop and a home server. The home server doesn’t need to be on the public internet, but mine is, for variety of reasons. This blog being one of them.
I get a static IP address from my ISP, Ucom. After the management change that happened couple of years ago, Ucom has become a very typical ISP (think shitty), but they are the only ones that provide a static IP address, instead of setting it on your router, where you have to do port forwarding.
My home server, hostnamed pingvinashen (meaning the town of the penguins, named after the Armenian cartoon) run FreeBSD. Historically this machine has run Debian, Funtoo, Gentoo and finally FreeBSD.
Hardware wise, here’s what it is:
root@pingvinashen:~ # dmidecode -s system-product-name
Latitude E5470
root@pingvinashen:~ # sysctl hw.model
hw.model: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6820HQ CPU @ 2.70GHz
root@pingvinashen:~ # sysctl hw.physmem
hw.physmem: 17016950784
root@pingvinashen:~ # zpool list
NAME SIZE ALLOC FREE CKPOINT EXPANDSZ FRAG CAP DEDUP HEALTH ALTROOT
zroot 420G 178G 242G - - 64% 42% 1.00x ONLINE -
While most homelabbers use hardware virtualization, I think that resources are a tight thing, and should be managed properly. Any company that markets itself as “green/eco-friendly” and uses hardware virtualization should do calculations using a pen and paper and prove if going native would save power/resources or not. (sometimes it doesn’t, usually it does)
I use containers, the old-school ones, Jails to be more specific.
I manage jails using Jailer, my own tool, that tries to stay out of your way when working with Jails.
Here are my current jails:
root@pingvinashen:~ # jailer list
NAME STATE JID HOSTNAME IPv4 GW
antranig Active 1 antranig.bsd.am 192.168.10.42/24 192.168.10.1
antranigv Active 2 antranigv.bsd.am 192.168.10.52/24 192.168.10.1
git Stopped
huginn0 Active 4 huginn0.bsd.am 192.168.10.34/24 192.168.10.1
ifconfig Active 5 ifconfig.bsd.am 192.168.10.33/24 192.168.10.1
lucy Active 6 lucy.vartanian.am 192.168.10.37/24 192.168.10.1
mysql Active 7 mysql.antranigv.am 192.168.10.50/24 192.168.10.1
newsletter Active 8 newsletter.bsd.am 192.168.10.65/24 192.168.10.1
oragir Active 9 oragir.am 192.168.10.30/24 192.168.10.1
psql Active 10 psql.pingvinashen.am 192.168.10.3/24 192.168.10.1
rss Active 11 rss.bsd.am 192.168.10.5/24 192.168.10.1
sarian Active 12 sarian.am 192.168.10.53/24 192.168.10.1
syuneci Active 13 syuneci.am 192.168.10.60/24 192.168.10.1
znc Active 14 znc.bsd.am 192.168.10.152/24 192.168.10.1
You already get a basic idea of how things are. Each of my blogs (Armenian and English) has its own Jail. Since I’m using WordPress, I need a database, so I have a MySQL jail (which ironically runs MariaDB) inside of it.
I also have a Git server, running gitea, which is down at the moment as I’m doing maintanence. The Git server (and many other services) requires PostgreSQL, hence the existence of a PostgreSQL jail. I run huginn for automation (RSS to Telegram, RSS to XMPP). My sister has her own blog, using WordPress, so that’s a Jail of its own. Same goes about my fiancée.
Other Jails are Newsletter using Listmonk, Sarian (the Armenian instance of lobste.rs) and a personal ZNC server.
As an avid RSS advocate, I also have a RSS Jail, which runs Miniflux. Many of my friends use this service.
Oragir is an instance of WriteFreely, as I advocate public blogging and ActivityPub. Our community uses that too.
The web server that forwards all this traffic from the public to the Jails is nginx. All it does is proxy_pass as needed. It runs on the host.
Other services that run on the host are DNS (BIND9), an email service running OpenSMTPd (which will be moved to a Jail soon), the chat service running prosody (which will be moved to a Jail soon) and finally, WireGuard, because I love VPNs.
Finally, there’s a IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnel that I use to obtain IPv6 thanks to Hurricane Electric.
Yes, I have a firewall, I use pf(4).
For the techies in the room, here’s what my rc.conf looks like.
# cat /etc/rc.conf
# Defaults
clear_tmp_enable="YES"
syslogd_flags="-ss"
sendmail_enable="NONE"
#local_unbound_enable="YES"
sshd_enable="YES"
moused_enable="YES"
ntpd_enable="YES"
# Set dumpdev to "AUTO" to enable crash dumps, "NO" to disable
dumpdev="AUTO"
zfs_enable="YES"
hostname="pingvinashen.am"
# Networking
defaultrouter="37.157.221.1"
gateway_enable="YES"
ifconfig_em0="up"
vlans_em0="37 1000" # 1000 -> WAN; 37 -> Home Router
ifconfig_em0_1000="inet 37.157.221.130 netmask 255.255.255.0"
ifconfig_em0_37="inet 192.168.255.2 netmask 255.255.255.0"
static_routes="home"
route_home="-net 172.16.100.0/24 -gateway 192.168.255.1"
cloned_interfaces="bridge0 bridge6 bridge10"
ifconfig_bridge10="inet 192.168.10.1 netmask 255.255.255.0"
## IPv6
ipv6_gateway_enable="YES"
gif_interfaces="gif0"
gifconfig_gif0="37.157.221.130 216.66.84.46"
ifconfig_gif0="inet6 2001:470:1f14:ef::2 2001:470:1f14:ef::1 prefixlen 128"
ipv6_defaultrouter="2001:470:1f14:ef::1"
ifconfig_em0_37_ipv6="inet6 2001:470:7914:7065::2 prefixlen 64"
ipv6_static_routes="home guest"
ipv6_route_home="-net 2001:470:7914:6a76::/64 -gateway 2001:470:7914:7065::1"
ipv6_route_guest="-net 2001:470:7914:6969::/64 -gateway 2001:470:7914:7065::1"
ifconfig_bridge6_ipv6="inet6 2001:470:1f15:e4::1 prefixlen 64"
ifconfig_bridge6_aliases="inet6 2001:470:1f15:e4::25 prefixlen 64 \
inet6 2001:470:1f15:e4::80 prefixlen 64 \
inet6 2001:470:1f15:e4::5222 prefixlen 64 \
inet6 2001:470:1f15:e4:c0fe::53 prefixlen 64 \
"
# VPN
wireguard_enable="YES"
wireguard_interfaces="wg0"
# Firewall
pf_enable="YES"
# Jails
jail_enable="YES"
jailer_dir="zfs:zroot/jails"
# DNS
named_enable="YES"
# Mail
smtpd_enable="YES"
smtpd_config="/usr/local/etc/smtpd.conf"
# XMPP
prosody_enable="YES"
turnserver_enable="YES"
# Web
nginx_enable="YES"
tor_enable="YES"
The gif0 interface is a IPv6-over-IPv4 tunnel. I have static routes to my home network, so I don’t go to my server over the ISP every time. This also gives me the ability to get IPv6 in my home network that is routed via my home server.
As you have guessed from this config file, I do have VLANs setup. So let’s get into that.
The Home Network
First of all, here’s a very cheap diagram
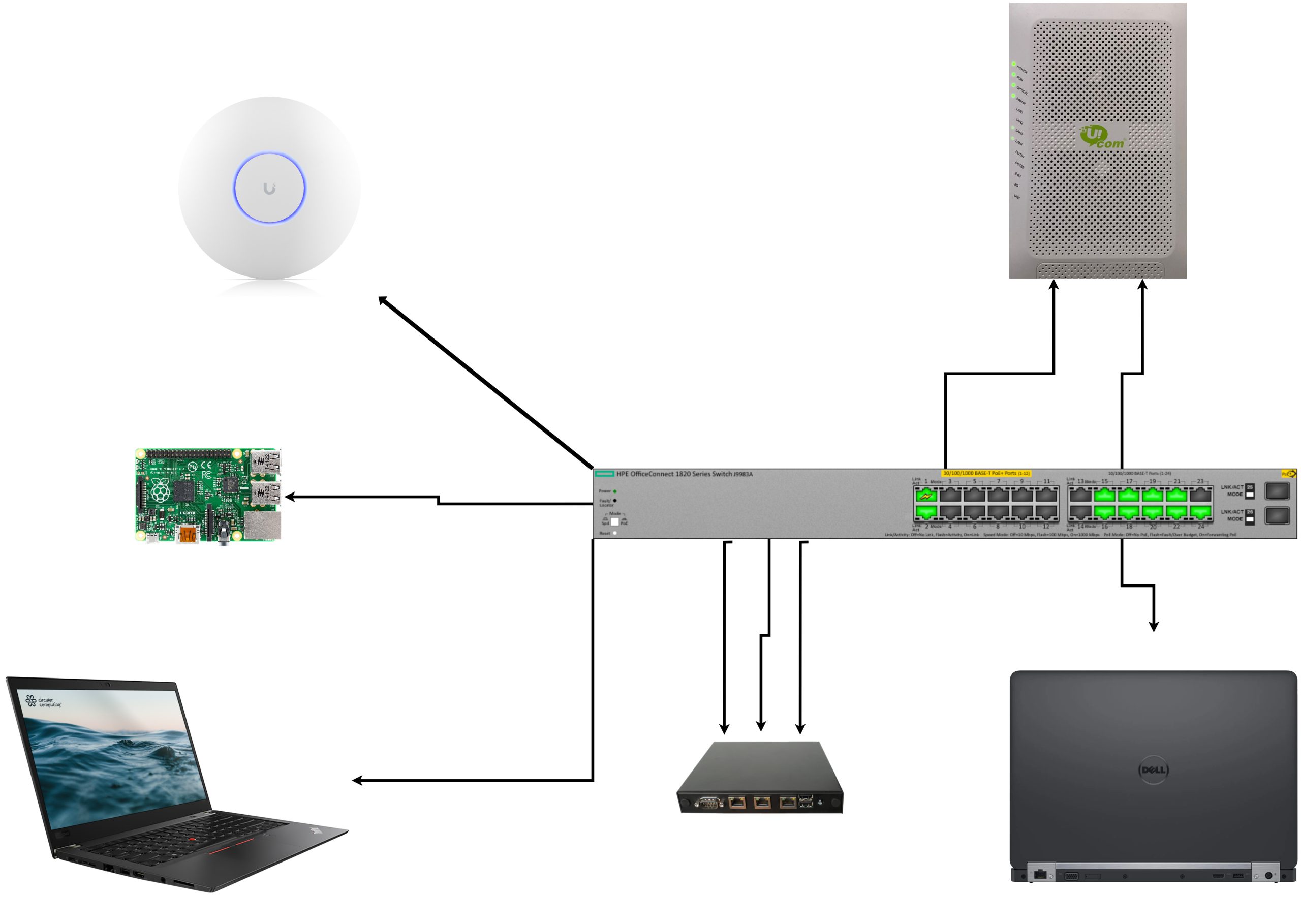
I have the following VLANs setup on the switch.
| VLAN ID |
Purpose |
| 1 |
Switch Management |
| 1000 |
pingvinashen (home server) WAN |
| 1001 |
evn0 (home router) WAN |
| 37 |
pingvinashen ↔ evn0 |
| 42 |
Internal Management |
| 100 |
Home LAN |
| 69 |
Home Guest |
Here are the active ports
| Port |
VLANs |
Purpose |
| 24 |
untagged: 1 |
Switch management, connects to Port 2 |
| 22 |
untagged: 1000 |
pingvinashen WAN, from ISP |
| 21 |
untagged: 1001 |
Home WAN, from ISP |
| 20 |
tagged: 1000, 37 |
To pingvinashen, port em0 |
| 19 |
untagged: 1001 |
To home router, port igb1 |
| 18 |
tagged: 42, 100, 69, 99 |
To home router, port igb2 |
| 17 |
untagged: 37 |
To home router, port igb0 |
| 16 |
tagged: 42, 100, 69 |
To Lenovo T480s |
| 15 |
untagged: 100 |
To Raspberri Pi 4 |
| 2 |
untagged: 99 |
From Port 24, for switch management |
| 1 |
untagged: 42; tagged: 100, 69; PoE |
To UAP AC Pro |
The home router, hostnamed evn0 (named after the IATA code of Yerevan’s Zvartnots International Airport) runs FreeBSD as well, the hardware is the following
root@evn0:~ # dmidecode -s system-product-name
APU2
root@evn0:~ # sysctl hw.model
hw.model: AMD GX-412TC SOC
root@evn0:~ # sysctl hw.physmem
hw.physmem: 4234399744
root@evn0:~ # zpool list
NAME SIZE ALLOC FREE CKPOINT EXPANDSZ FRAG CAP DEDUP HEALTH ALTROOT
zroot 12.5G 9.47G 3.03G - - 67% 75% 1.00x ONLINE -
The home router does… well, routing. It also does DHCP, DNS, SLAAC, and can act as a syslog server.
Here’s what the rc.conf looks like
clear_tmp_enable="YES"
sendmail_enable="NONE"
syslogd_flags="-a '172.16.100.0/24:*' -H"
zfs_enable="YES"
dumpdev="AUTO"
hostname="evn0.illuriasecurity.com"
pf_enable="YES"
gateway_enable="YES"
ipv6_gateway_enable="YES"
sshd_enable="YES"
# Get an IP address from the ISP's GPON
ifconfig_igb1="DHCP"
# Internal routes with pingvinashen
ifconfig_igb0="inet 192.168.255.1 netmask 255.255.255.0"
ifconfig_igb0_ipv6="inet6 2001:470:7914:7065::1 prefixlen 64"
static_routes="pingvinashen"
route_pingvinashen="-net 37.157.221.130/32 -gateway 192.168.255.2"
ipv6_defaultrouter="2001:470:7914:7065::2"
# Home Mgmt, Switch Mgmt, Home LAN, Home Guest
ifconfig_igb2="up"
vlans_igb2="42 99 100 69"
ifconfig_igb2_42="inet 172.31.42.1 netmask 255.255.255.0"
ifconfig_igb2_99="inet 172.16.99.1 netmask 255.255.255.0"
ifconfig_igb2_100="inet 172.16.100.1 netmask 255.255.255.0"
ifconfig_igb2_100_ipv6="inet6 2001:470:7914:6a76::1 prefixlen 64"
ifconfig_igb2_69="inet 192.168.69.1 netmask 255.255.255.0"
ifconfig_igb2_69_ipv6="inet6 2001:470:7914:6969::1 prefixlen 64"
# DNS and DHCP
named_enable="YES"
dhcpd_enable="YES"
named_flags=""
# NTP
ntpd_enable="YES"
# Router Advertisement and LLDP
rtadvd_enable="YES"
lldpd_enable="YES"
lldpd_flags=""
Here’s pf.conf, because security is important.
ext_if="igb1"
bsd_if="igb0"
int_if="igb2.100"
guest_if="igb2.69"
mgmt_if="igb2.42"
sw_if="igb2.99"
ill_net="172.16.0.0/16"
nat pass on $ext_if from $int_if:network to any -> ($ext_if)
nat pass on $ext_if from $mgmt_if:network to any -> ($ext_if)
nat pass on $ext_if from $guest_if:network to any -> ($ext_if)
set skip on { lo0 }
block in all
pass on $int_if from $int_if:network to any
pass on $mgmt_if from $mgmt_if:network to any
pass on $sw_if from $sw_if:network to any
pass on $guest_if from $guest_if:network to any
block quick on $guest_if from any to { $int_if:network, $mgmt_if:network, $ill_net, $sw_if:network }
pass in on illuria0 from $ill_net to { $ill_net, $mgmt_if:network }
pass inet proto icmp
pass inet6 proto icmp6
pass out all keep state
I’m sure there are places to improve, but it gets the job done and keeps the guest network isolated.
Here’s rtadvd.conf, for my IPv6 folks
igb2.100:\
:addr="2001:470:7914:6a76::":prefixlen#64:\
:rdnss="2001:470:7914:6a76::1":\
:dnssl="evn0.loc.illuriasecurity.com,loc.illuriasecurity.com":
igb2.69:\
:addr="2001:470:7914:6969::":prefixlen#64:\
:rdnss="2001:470:7914:6969::1":
For DNS, I’m running BIND, here’s the important parts
listen-on { 127.0.0.1; 172.16.100.1; 172.16.99.1; 172.31.42.1; 192.168.69.1; };
listen-on-v6 { 2001:470:7914:6a76::1; 2001:470:7914:6969::1; };
allow-query { 127.0.0.1; 172.16.100.0/24; 172.31.42.0/24; 192.168.69.0/24; 2001:470:7914:6a76::/64; 2001:470:7914:6969::/64;};
And for DHCP, here’s what it looks like
subnet 172.16.100.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 172.16.100.100 172.16.100.150;
option domain-name-servers 172.16.100.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option routers 172.16.100.1;
option domain-name "evn0.loc.illuriasecurity.com";
option domain-search "loc.illuriasecurity.com evn0.loc.illuriasecurity.com";
}
host zvartnots {
hardware ethernet d4:57:63:f1:5a:36;
fixed-address 172.16.100.7;
}
host unifi0 {
hardware ethernet 58:9c:fc:93:d1:0b;
fixed-address 172.31.42.42;
}
[…]
subnet 172.31.42.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 172.31.42.100 172.31.42.150;
option domain-name-servers 172.31.42.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option routers 172.31.42.1;
}
subnet 192.168.69.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.69.100 192.168.69.150;
option domain-name-servers 192.168.69.1;
option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0;
option routers 192.168.69.1;
}
So you’re wondering, what’s this unifi0? Well, that brings us to
T480s
This laptop has been gifted to me by [REDACTED] for my contributions to the Armenian government (which means when a server goes down and no one knows how to fix it, they called me and I showed up)
Here’s the hardware
root@t480s:~ # dmidecode -s system-version
ThinkPad T480s
root@t480s:~ # sysctl hw.model
hw.model: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-8350U CPU @ 1.70GHz
root@t480s:~ # sysctl hw.physmem
hw.physmem: 25602347008
root@t480s:~ # zpool list
NAME SIZE ALLOC FREE CKPOINT EXPANDSZ FRAG CAP DEDUP HEALTH ALTROOT
zroot 224G 109G 115G - - 44% 48% 1.00x ONLINE -
The T480s has access to VLAN 100, 42, 69, but the host itself has access only to VLAN 100 (LAN), while the jails can exist on other VLANs.
So I have a Jail named unifi0 that runs the Unifi Management thingie.
Here’s what rc.conf of the host looks like
clear_tmp_enable="YES"
syslogd_flags="-ss"
sendmail_enable="NONE"
sshd_enable="YES"
ntpd_enable="YES"
# Set dumpdev to "AUTO" to enable crash dumps, "NO" to disable
dumpdev="AUTO"
zfs_enable="YES"
hostname="t480s.evn0.loc.illuriasecurity.com"
ifconfig_em0="up -rxcsum -txcsum"
vlans_em0="100 42 69"
ifconfig_em0_100="up"
ifconfig_em0_42="up"
ifconfig_em0_69="up"
cloned_interfaces="bridge0 bridge100 bridge42 bridge69"
create_args_bridge100="ether 8c:16:45:82:b4:10"
ifconfig_bridge100="addm em0.100 SYNCDHCP"
ifconfig_bridge100_ipv6="inet6 auto_linklocal"
rtsold_flags="-i -F -m bridge100"
rtsold_enable="YES"
create_args_bridge42=" ether 8c:16:45:82:b4:42"
create_args_bridge69=" ether 8c:16:45:82:b4:69"
ifconfig_bridge42="addm em0.42"
ifconfig_bridge69="addm em0.69"
jail_enable="YES"
jailer_dir="zfs:zroot/jailer"
ifconfig_bridge0="inet 10.1.0.1/24 up"
ngbuddy_enable="YES"
ngbuddy_private_if="nghost0"
dhcpd_enable="YES"
lldpd_enable="YES"
I used Jailer to create the unifi0 jail, here’s what the jail.conf looks like
# vim: set syntax=sh:
exec.clean;
allow.raw_sockets;
mount.devfs;
unifi0 {
$id = "6";
devfs_ruleset = 10;
$bridge = "bridge42";
$domain = "evn0.loc.illuriasecurity.com";
vnet;
vnet.interface = "epair${id}b";
exec.prestart = "ifconfig epair${id} create up";
exec.prestart += "ifconfig epair${id}a up descr vnet-${name}";
exec.prestart += "ifconfig ${bridge} addm epair${id}a up";
exec.start = "/sbin/ifconfig lo0 127.0.0.1 up";
exec.start += "/bin/sh /etc/rc";
exec.stop = "/bin/sh /etc/rc.shutdown jail";
exec.poststop = "ifconfig ${bridge} deletem epair${id}a";
exec.poststop += "ifconfig epair${id}a destroy";
host.hostname = "${name}.${domain}";
path = "/usr/local/jailer/unifi0";
exec.consolelog = "/var/log/jail/${name}.log";
persist;
mount.fdescfs;
mount.procfs;
}
Here are the important parts inside the jail
root@t480s:~ # cat /usr/local/jailer/unifi0/etc/rc.conf
ifconfig_epair6b="SYNCDHCP"
sendmail_enable="NONE"
syslogd_flags="-ss"
mongod_enable="YES"
unifi_enable="YES"
root@t480s:~ # cat /usr/local/jailer/unifi0/etc/start_if.epair6b
ifconfig epair6b ether 58:9c:fc:93:d1:0b
Don’t you love it that you can see what’s inside the jail from the host? God I love FreeBSD!
Did I miss anything? I hope not.
Oh, for the homelabbers out there, the T480s is the one that runs things like Jellyfin if needed.
Finally, the tiny
Raspberry Pi 4, Model B
I found this in a closed, so I decided to run it for TimeMachine.
I guess all you care about is rc.conf
hostname="tm0.evn0.loc.illuriasecurity.com"
ifconfig_DEFAULT="DHCP inet6 accept_rtadv"
sshd_enable="YES"
sendmail_enable="NONE"
sendmail_submit_enable="NO"
sendmail_outbound_enable="NO"
sendmail_msp_queue_enable="NO"
growfs_enable="YES"
powerd_enable="YES"
# Set dumpdev to "AUTO" to enable crash dumps, "NO" to disable
dumpdev="AUTO"
zfs_enable="YES"
rtsold_enable="YES"
samba_server_enable="YES"
And the Samba Configuration
[global]
# Network settings
workgroup = WORKGROUP
server string = Samba Server %v
netbios name = RPi4
# Logging
log file = /var/log/samba4/log.%m
max log size = 50
log level = 0
# Authentication
security = user
encrypt passwords = yes
passdb backend = tdbsam
map to guest = Bad User
min protocol = SMB2
max protocol = SMB3
# Apple Time Machine settings
vfs objects = catia fruit streams_xattr
fruit:metadata = stream
fruit:resource = stream
fruit:encoding = native
fruit:locking = none
fruit:time machine = yes
# File System support
ea support = yes
kernel oplocks = no
kernel share modes = no
posix locking = no
mangled names = no
smbd max xattr size = 2097152
# Performance tuning
read raw = yes
write raw = yes
getwd cache = yes
strict locking = no
# Miscellaneous
local master = no
preferred master = no
domain master = no
wins support = no
[tm]
comment = Time Machine RPi4
path = /usr/local/timemachine/%U
browseable = yes
read only = no
valid users = antranigv
vfs objects = catia fruit streams_xattr
fruit:time machine = yes
fruit:advertise_fullsync = true
fruit:time machine max size = 800G # Adjust the size according to your needs
create mask = 0600
directory mask = 0700
That’s pretty much it.
Conclusion
I love running homebrew servers, home networks and home labs. I love that (almost) everything is FreeBSD. The switch itself runs Linux, and the Unifi Access Point also runs Linux, both of which I’m pretty happy with.
While most homelabbers used ESXi in the past, I’m happy to see that most people are moving to open source solutions like Proxmox and Xen, but I think that FreeBSD Jails and bhyve is much better. I still don’t have a need for bhyve at the moment, but I would use it if I needed hardware virtualization.
Most homelabbers would consider the lack of Web/GUI interfaces as a con, but I think that it’s a pro. If I need to “replicate” this network, all I need to do is to copy some text files and modify some IP addresses / Interface names.
I hope this was informative and that it would be useful for anyone in the future.
That’s all folks…
